Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus completes posttranslational modifications of proteins produced in the rough endoplasmic retirculum and then packages and addresses these proteins to their proper destinations.1
The organelle was named after Italian Camillo Golgi who discovered it in 1898.

The Golgi apparatus consists of many smooth membranous saccules, some vesicular, others flattened, but all containing enzymes and proteins being processed.
In most cells the small Golgi complexes are located near the nucleus.
The Golgi apparatus packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It is part of the cellular endomembrane system. The Golgi apparatus resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways.
. It is another packaging organelle like the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
The Golgi apparatus gathers simple molecules and combines them to make molecules that are more complex. It then takes those big molecules, packages them in vesicles, and either stores them for later use or sends them out of the cell. It is also the organelle that builds lysosomes (cell digestion machines).
{Golgi complexes in the plant may also create complex sugars and send them off in secretory vesicles. The vesicles are created in the same way the ER does it. The vesicles are pinched off the membranes and float through the cell.} IEA: can plants makes molecules that are deficient in human cells!!!!!
[Tobacco used to produce antibodies]
The Golgi apparatus is a series of membranes.. The single membrane is similar to the cell membrane in that it has two layers. The membrane surrounds an area of fluid where the complex molecules (proteins, sugars, enzymes) are stored and changed. Because the Golgi complex absorbs vesicles from the rough ER, you will also find ribosomes in membrance.
Working with the Rough ER
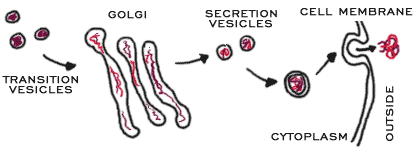
The Golgi complex works closely with the rough ER. When a protein is made in the ER, something called a transition vesicle is made. This vesicle or sac floats through the cytoplasm to the Golgi apparatus and is absorbed. After the Golgi does its work on the molecules inside the sac, a secretory vesicleis created and released into the cytoplasm. From there, the vesicle moves to the cell membrane and the molecules are released out of the cell.
It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus.
The Golgi apparatus was discovered in 1898 by Italian physician Camillo Golgi during an investigation of the nervous system.[1][2] The term "Golgi apparatus" was used in 1910 and first appeared in the scientific literature in 1913.[2]
Content 2
Content 3

Micrograph Golgi apparatus, stack of semicircular rings; circular vesicles seen in proximity of organelle
Study Questions
Which pair of functions is associated with the Golgi complex?
The correct answer is D.
Content 2
Content 3